This list is non-exhaustive and new genes will continue to be added as the game grows!
This page hosts information and examples of each marking gene. Markings give your phony patterns and a lot of individual flair, and there's several ways that each gene can be expressed for plenty of freedom.
There are three layers of markings: Bottom, Middle and Top.
- Bottom layer markings are often large, simplistic markings which other markings are layered on top of. Most of them can be soft or hard edged.
- Middle layer markings are interesting patterns which go on top of the more simple markings. They are all hard edged.
- Top layer markings are small detail-oriented markings which go on top of every other marking. They are all hard edged.
What does zygousness mean?
- Heterozygous means you have one copy of the allele for the gene. This expresses in your phony's geno as one uppercase and one lowercase letter. (e.g. Bk, Cs, Re...) Heterozygous genes may or may not pass onto offspring, depending on the genotype of the other phony. Heterozygous genes are single solid colored.
- Homozygous means you have both copies of the allele for the gene. This expresses in your phony's geno as two uppercase letters. (e.g. BK, CS, RE...) Homozygous genes always pass onto the offspring. Homozygous genes can have as many colors in them as desired, as long as the phony has those colors in its personal color bank, and that can present in a number of ways. The homozygous marking can be a gradient, or solid color but duotoned, and so on.
What's the difference between hard and soft edged?
- Hard Edged refers to markings which have a solid edge. They aren't blurry or smudgy.
- Soft Edged refers to markings which have a blurred, soft edge. They shouldn't be too crisp.
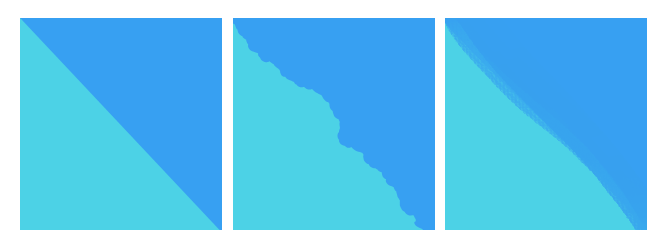
#1 - A solid hard edge. #2 - A "crunchy" hard edge. #3 - A painterly hard edge. This one approaches the boundary between hard and soft edged, so tread carefully and be prepared for revisions if you go with this style.
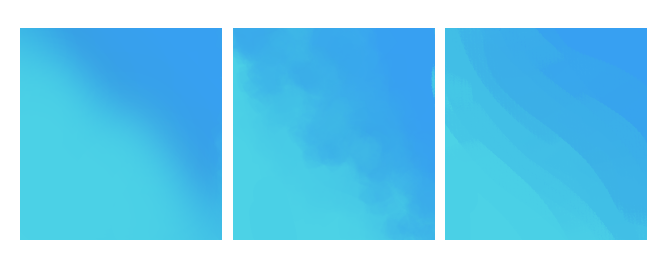
#1 - A classic airbrushed soft edge. #2 - A more irregular, dappled soft edge. #3 - A more layered soft edge, where you can somewhat see the variations in color.
Bottom Layer Markings
Blanket (Bk)
Blanket is a dominant gene which makes a marking on the back of the phony. This would include the spine, tops of legs, back of neck and top of head.
- Can be hard or soft edged
- Single color if heterozygous (Bk) or multicolor if homozygous (BK)
This marking is affected by the tri-symmetry mutation. See more here.
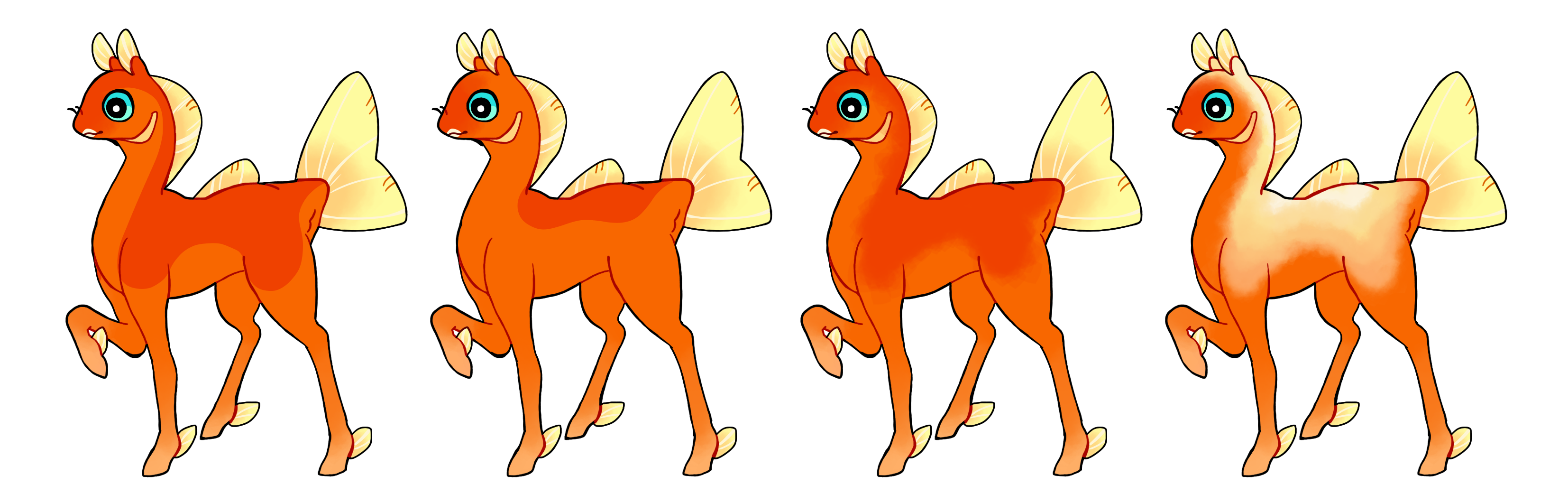

#1 - Blanket covering a large area with a hard edge
#2 - Blanket covering a smaller area with a hard edge
#3 - Blanket with a soft edge
#4 - Homozygous blanket with a soft edge and multiple colors
Countershade (Cs)
Countershade is a dominant gene which makes a marking on the underside of the phony.
- Can be hard or soft edged
- Single color if heterozygous (Cs) or multicolor if homozygous (CS)
This marking is affected by the tri-symmetry mutation. See more here.
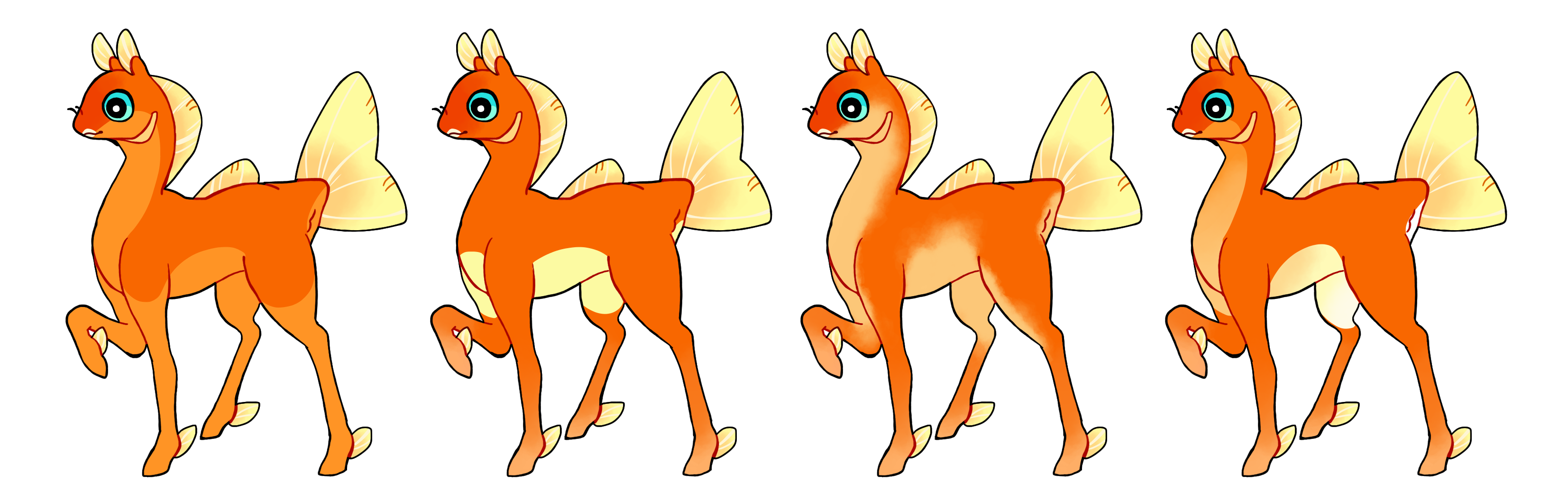

#1 - Countershade covering a large area with a hard edge
#2 - Countershade covering a small area with a hard edge
#3 - Countershade with a soft edge
#4 - Homozygous countershade with a hard edge and multiple colors
Rear (Re)
Rear is a dominant gene which covers the rear end of a phony to about halfway through the torso. Like a pair of pants!
- Can be hard or soft edged
- Single color if heterozygous (Re) or multicolored if homozygous (RE)
See here for examples of this marking on phonies with no distinct back end.
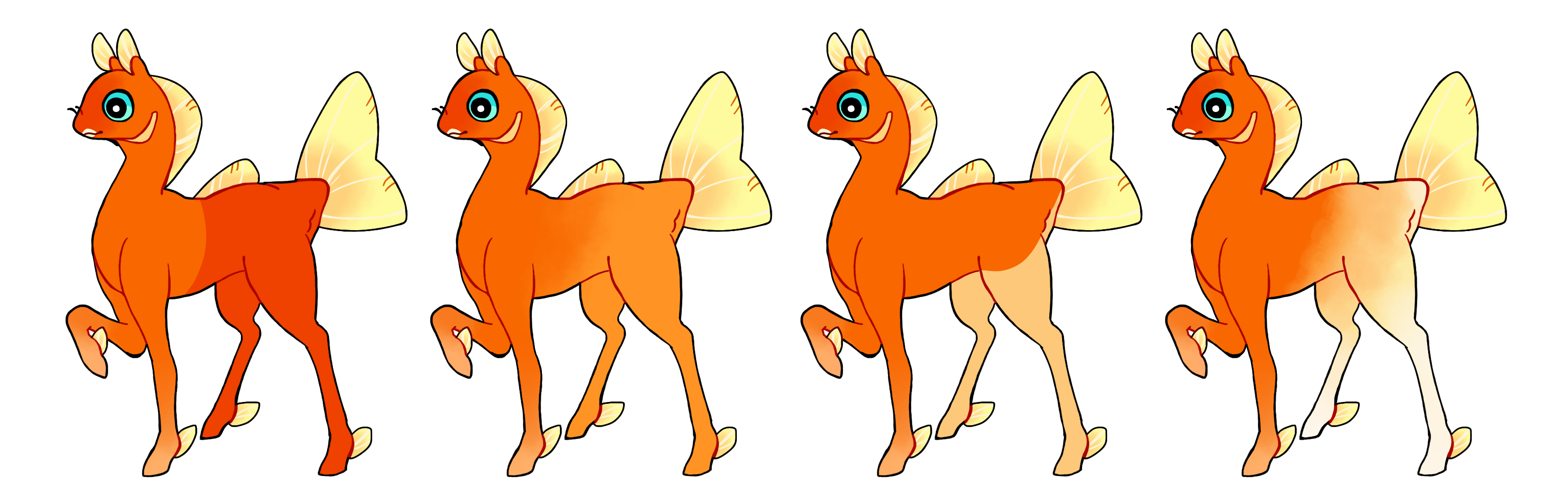

#1 - Rear with a hard edge
#2 - Rear with a soft edge
#3 - Rear covering a smaller area with a hard edge
#4 - Homozygous rear with a soft edge and multiple colors
Sweater (Sw)
Sweater is a dominant gene which covers the front of the phony from the torso to the face. Like a sweater! It should wrap around the shoulders, and be one continuous marking.
- Can be hard or soft edged
- Single color if heterozygous (Sw) or multicolored if homozygous (SW)
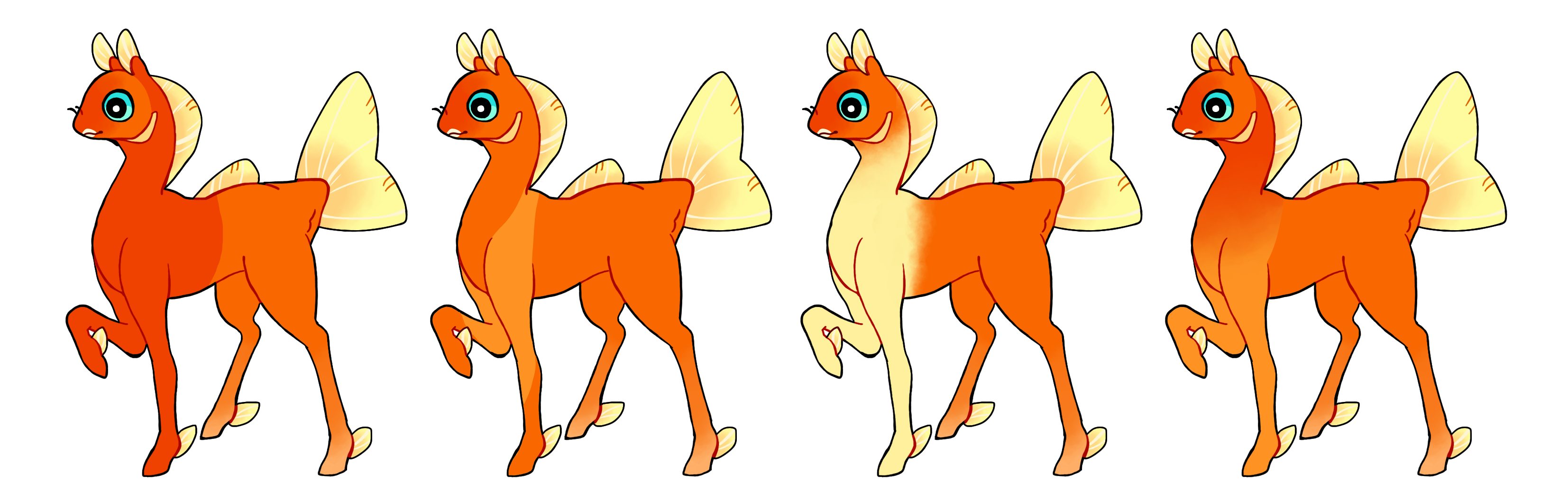

#1 - Sweater with maximum coverage and a hard edge
#2 - Sweater with minimum coverage and a hard edge
#3 - Sweater with a soft edge.
#4 - Homozygous sweater with a hard edge and a gradient.
Hood (Ho)
Hood is a dominant gene which covers the head of the phony and optionally the neck. This marking can be simple or more intricate.
- Can be hard or soft edged
- Single color if heterozygous (Ho) or multicolored if homozygous (HO)
#1 - Hood covering the maximum allowed area in a simple shape
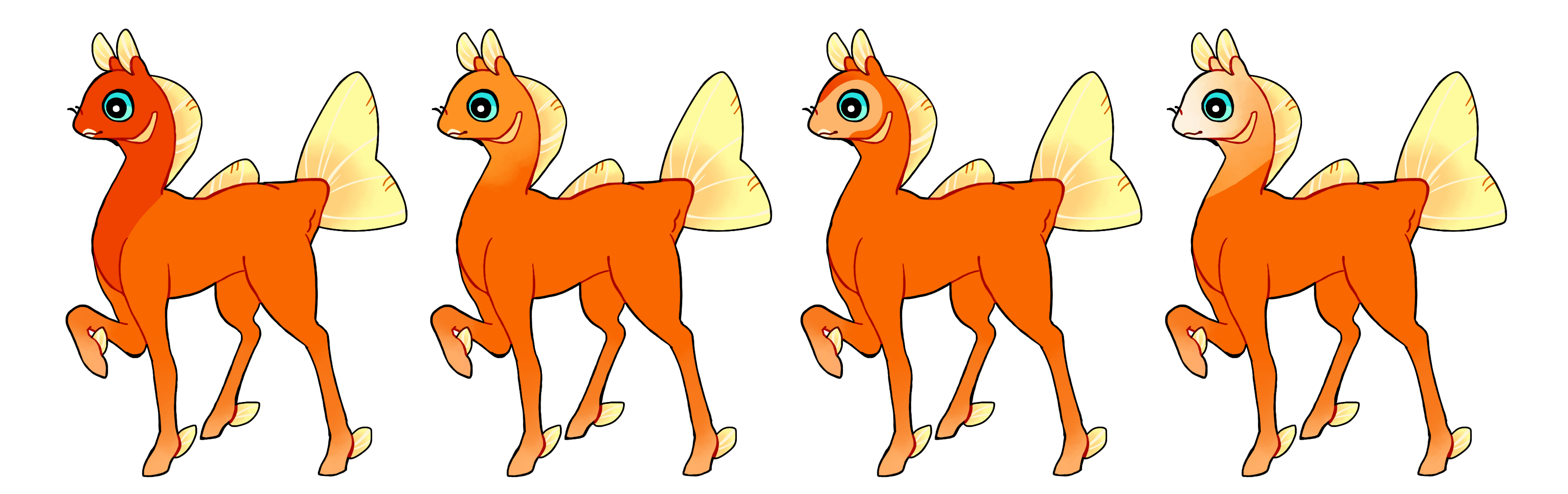

#1 - Hood with a hard edge and maximum coverage
#2 - Hood with a soft edge
#3 - Hood covering a smaller area with a hard edge
#4 - Homozygous hood with a hard edge and multiple colors
Saddle (Sd)
Saddle is a dominant gene which covers the back of a phony similarly to blanket, except it includes a bar which wraps around the phony's belly.
- Always hard edged
- Single color if heterozygous (Sd) or multicolored if homozygous (SD)
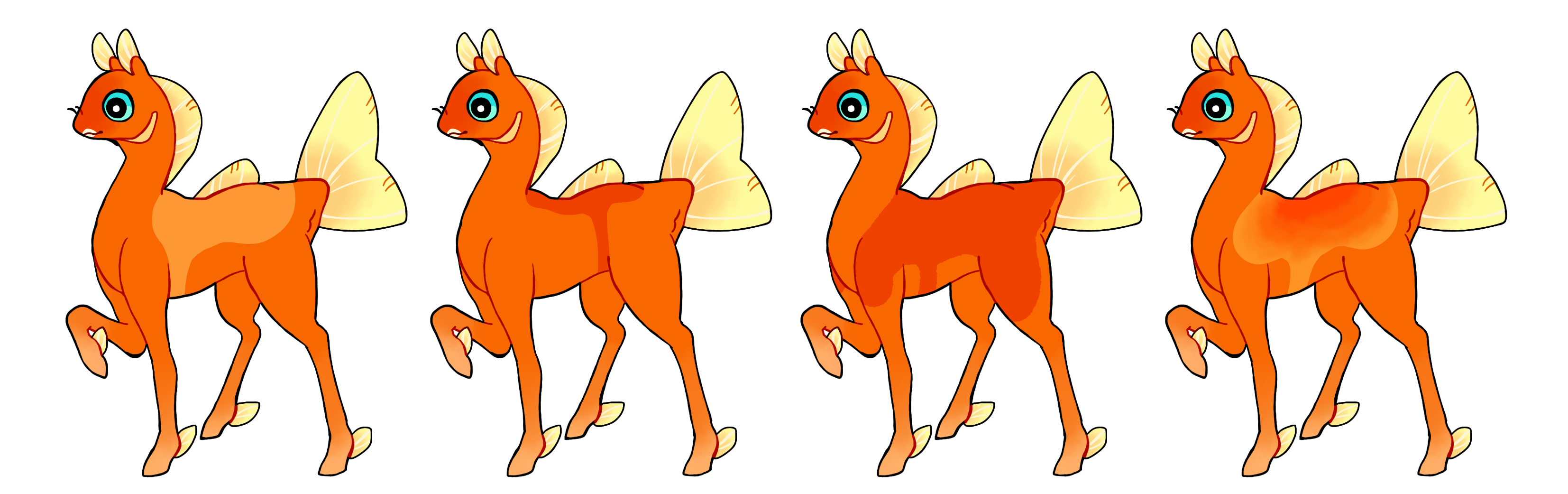

#1 - Saddle.
#2 - Saddle with minor coverage.
#3 - Saddle with large coverage.
#4 - Homozygous saddle with a gradient.
Blushed (Bl)
Blushed is a dominant gene which covers the extremities of a phony, such as the mouth and feet.
- Always soft edged
- Single color if heterozygous (Bl) or multicolored if homozygous (BL)
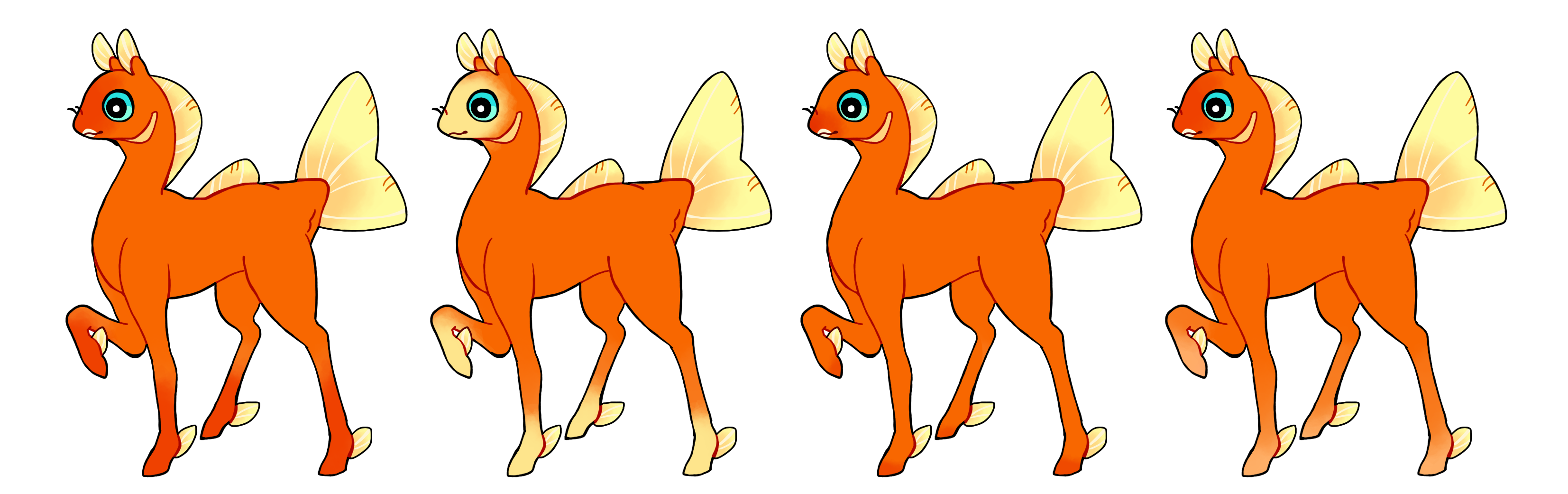

#1 - Blushed
#2 - Blushed
#3 - Blushed with less coverage
#4 - Homozygous blushed with multiple colors
Diffuse (Ds)
Diffuse is a dominant gene which creates large soft markings in any shape anywhere on the body. It should not mimic other baselayer markings.
- Always soft edged
- Single color if heterozygous (Ds) or multicolored if homozygous (DS)
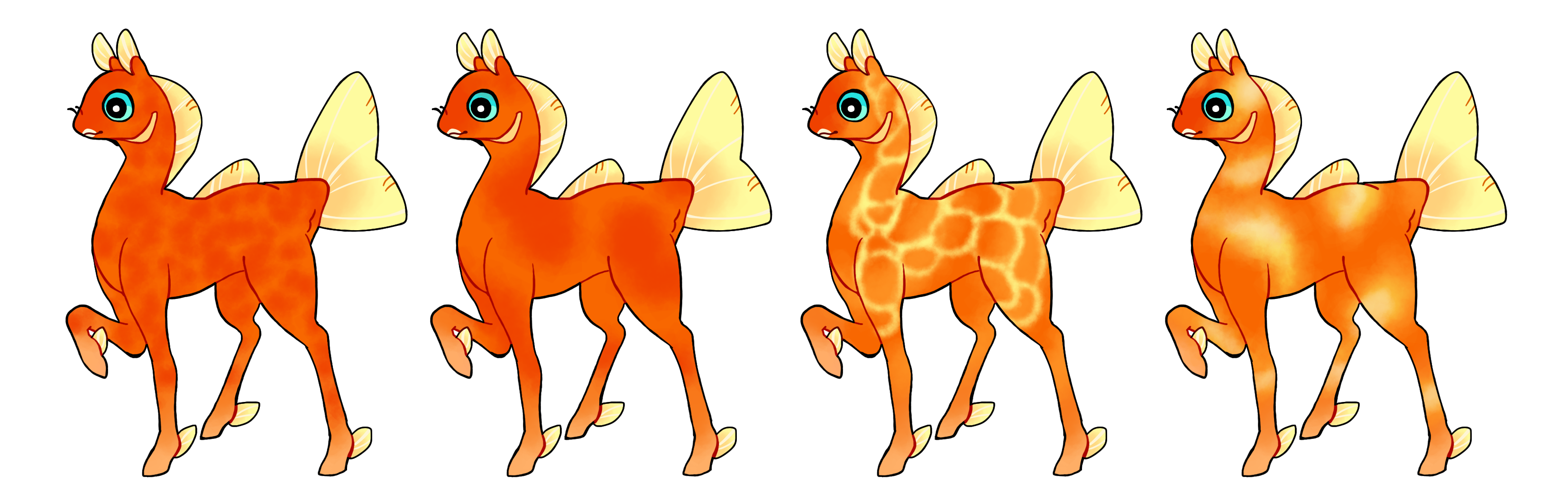

#1 - Diffuse creating soft dappling
#2 - Diffuse creating large soft patches
#3 - Homozygous diffuse with one soft broad layer and a more intricate ripply layer in a different color
#4 - Homozygous diffuse with multiple colors
Middle Layer Markings
Lateral Stripe (Ls)
Lateral Stripe is a dominant gene that creates a hard edged stripe along the side of the phony. It can be split into two chunks if desired. Lateral Stripe should not wrap around the whole phony (that's what linework is for!), it should taper off. Single colored if heterozygous (Ls) or multicolored if homozygous (LS).
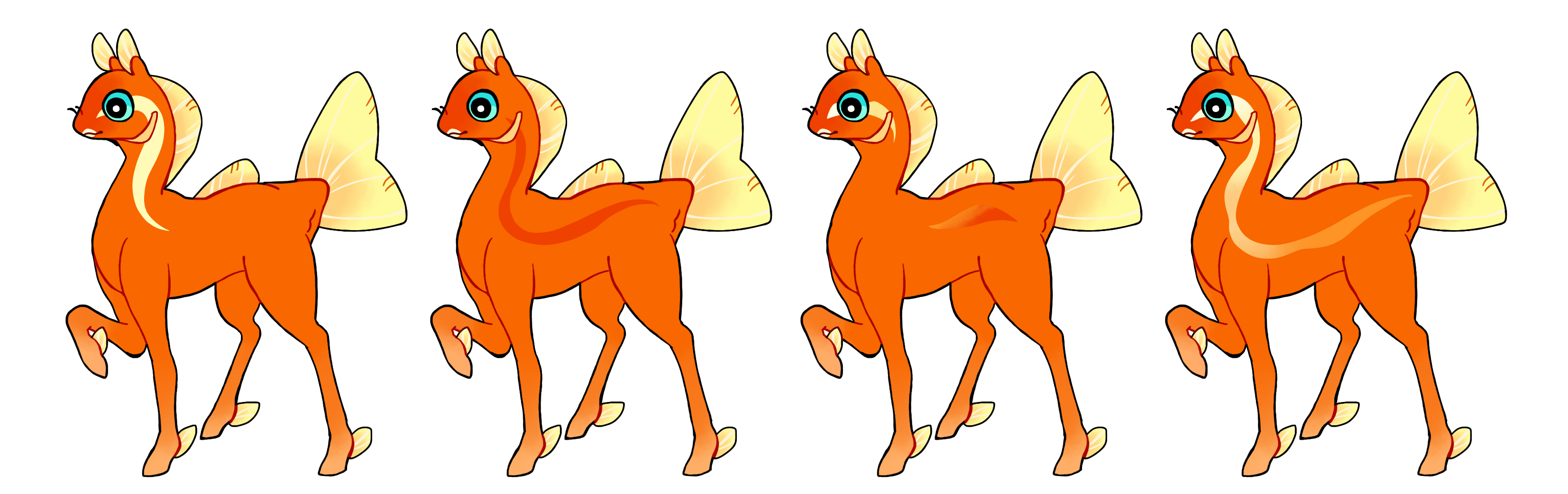

#1 - Lateral stripe
#2 - Lateral stripe
#3 - Homozygous lateral stripe in two chunks with a gradient.
#4 - Homozygous lateral stripe with a gradient going along the whole phony's length.
Dorsal (Do)
Dorsal is a dominant gene that creates a hard edged marking that covers the spine. It also doesn't need to extend down the entire spine. Single color if heterozygous (Do) or multicolored if homozygous (DO). Historically this marking has added toe markings, but as those are minimal markings now, you can add those even if you don't have dorsal.
This marking is affected by the tri-symmetry mutation. See more here.
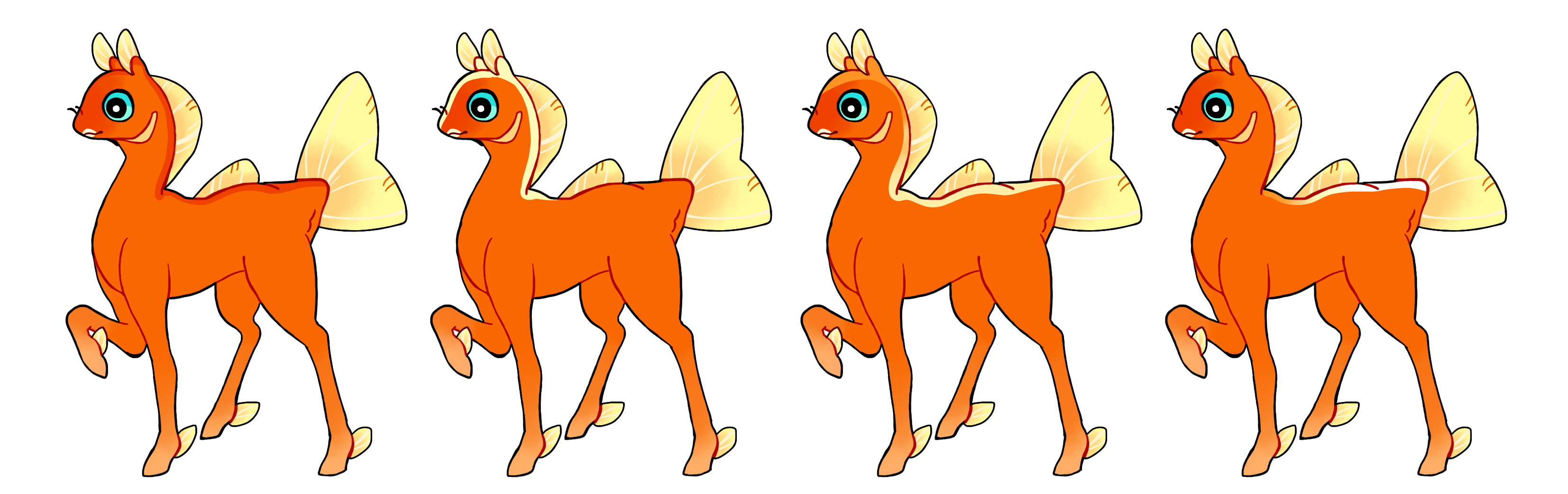

#1 - Dorsal
#2 - Dorsal covering just to the neck
#3 - Homozygous dorsal with a gradient
#4 - Homozygous dorsal with a gradient, only covering after the neck
Socks (So)
Socks is a dominant gene that creates a hard edged marking that covers the feet and legs. It doesn't need to cover all feet, in fact it can only cover one or two of them, but it shouldn't be so small in size that it mimics minimal marking toetips. Heterozygous socks (So) must be a single color and homozygous socks (SO) may be multicolored.
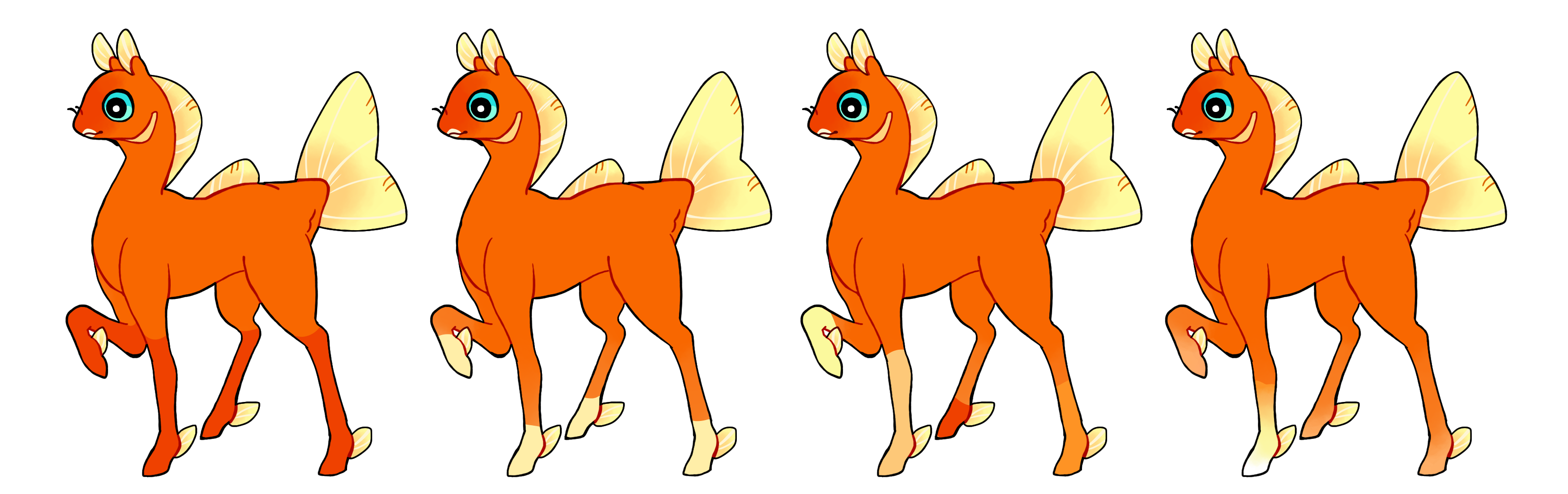

#1 - Long socks
#2 - Short socks
#3 - Homozygous socks, each with different colors
#4 - Homozygous socks with just one sock and a gradient in it
Koi (Ko)
Koi is a dominant gene that creates hard edged splotches of any quantity, anywhere on the phony. Single-colored if heterozygous (Ko) or multicolored if homozygous (KO).
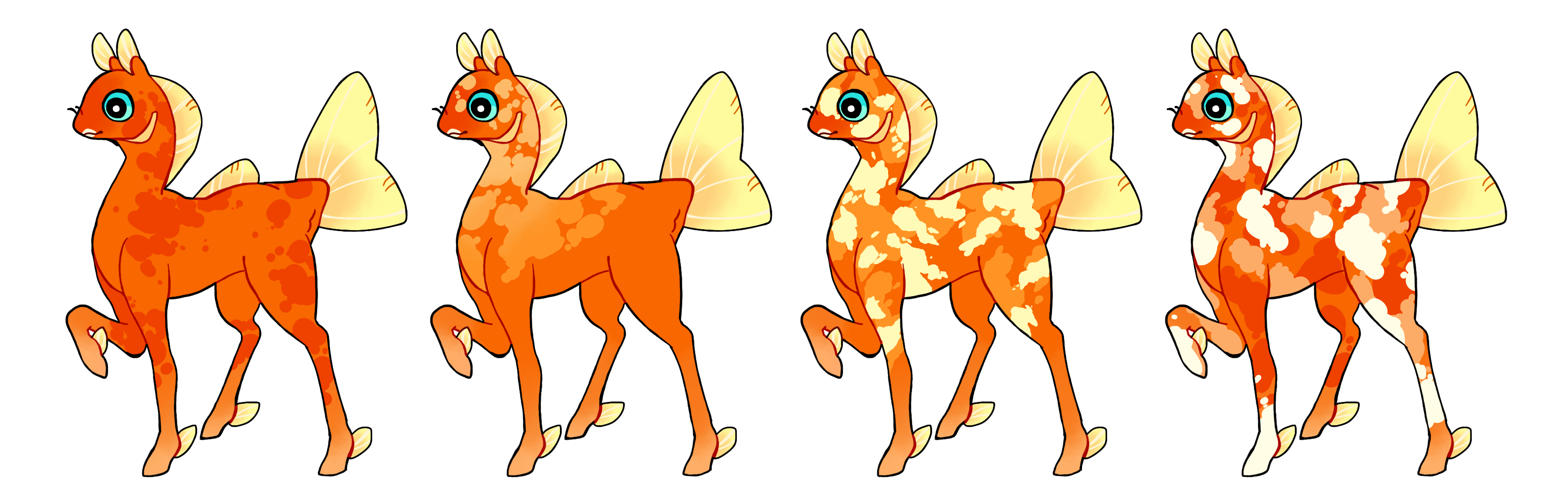

#1 - Koi.
#2 - Homozygous koi with a gradient.
#3 - Homozygous koi with duotone splotches.
#4 - Homozygous koi with tritone splotches.
Spots (Sp)
Spots is a dominant gene that creates hard edged round markings. The spots can be of any frequency and size as long as they don't mimic other markings like stars, scales or koi. Spots also cannot touch each other to create new shapes. Single color if heterozygous (Sp) or multicolored if homozygous (SP)
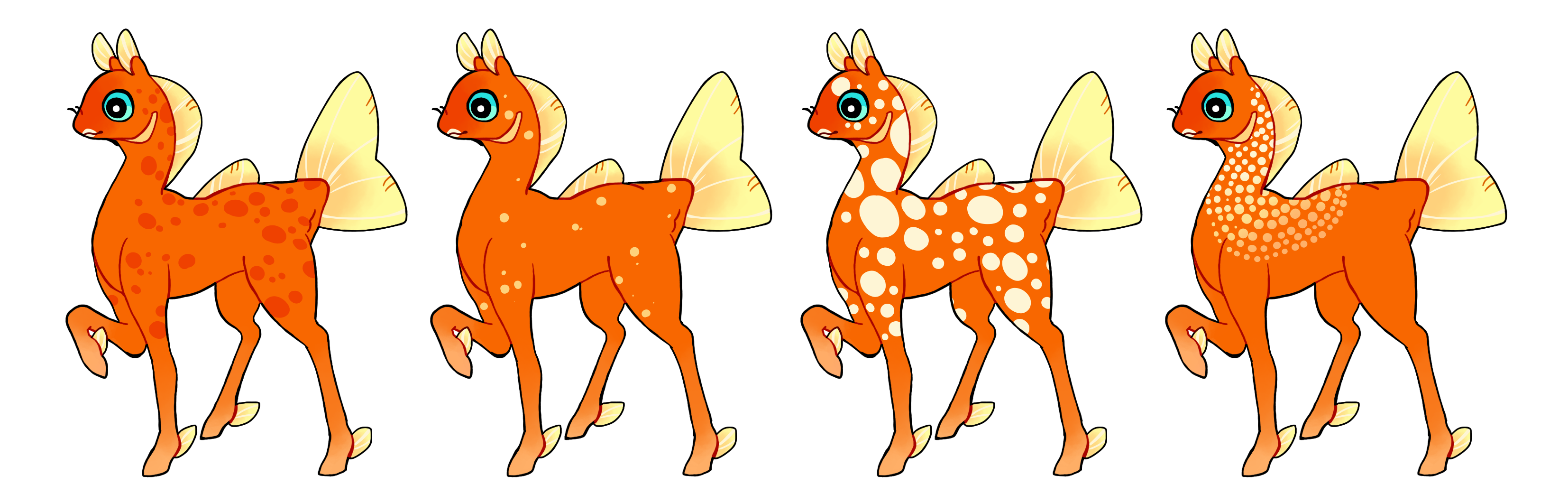

#1 - Spots
#2 - Smaller and more infrequent spots
#3 - Larger spots
#4 - Homozygous spots with a gradient
Scales (Sc)
Scales is a dominant gene that creates hard edged scale shaped markings on the phony. They may mimic any type of scale as long as it doesn't look too much like another marking such as spots or giraffe. Single colored if heterozygous (Sc) and multicolored if homozygous (SC).
The "Paint" gene was recently merged into Scales. Phonies with Paint will pass on Scales when breeding instead.
Phonies on the ML with Pt can request their genotype be updated to include Sc instead in the Import Modifications thread, and you can do the same for genotypes in the Geno Edits thread. Existing phonies can only get a visible redesign if they use an editor vial while updating the geno.
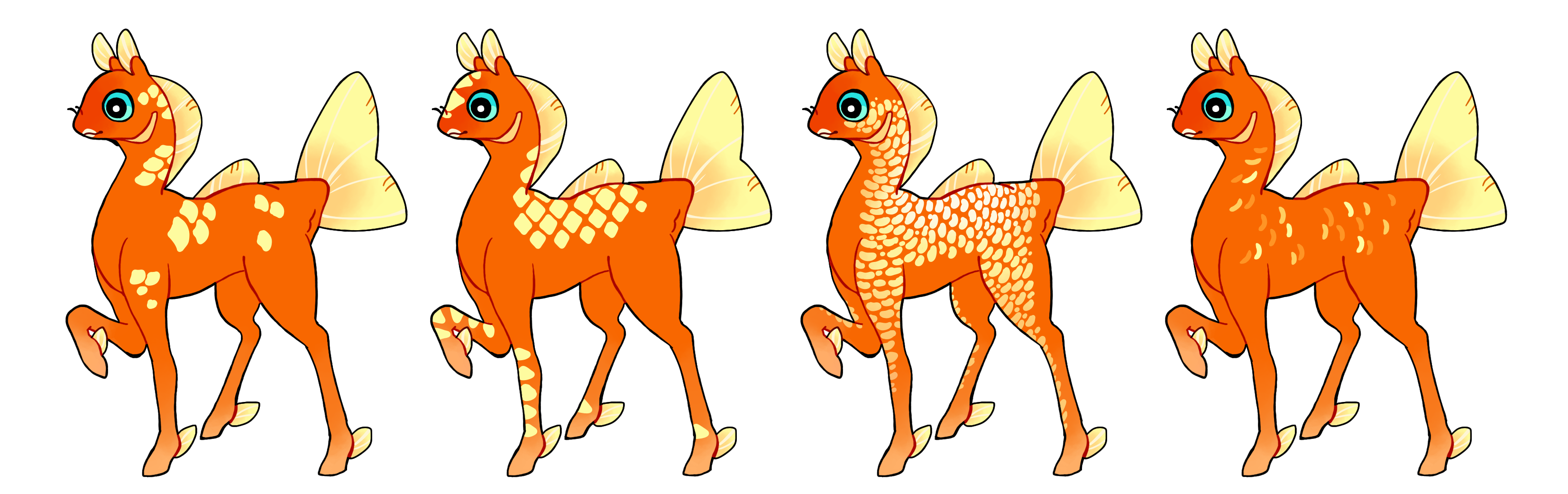

#1 - Scales like a carp's.
#2 - Diamond-shaped scales with scutes on the legs and face.
#3 - Homozygous scales with a gradient, with bean-shaped scales. Paint used to express like this.
#4 - Homozygous stylized scales, each a different color.
Rosettes (Ro)
Rosettes is a dominant gene that creates many hard edged intricate rosette-shaped markings anywhere on the phony's body. They can be mimicking some animal patterns like leopard spots or turing patterns, or they can be more abstract as long as they have a degree of complexity/intricacy/detail/wigglysquigglyness to them. Single color if heterozygous (Ro) or multicolored if homozygous (RO). Hom rosettes can fill in hollow spots with a different color if desired.
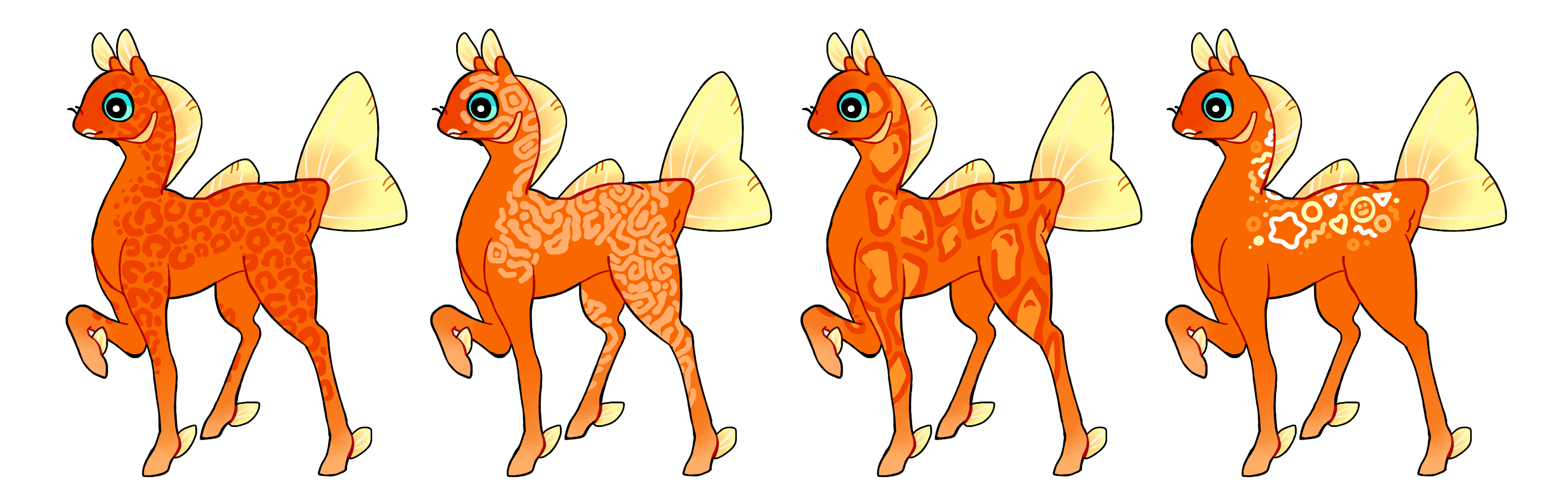

#1 - Rosettes, mimicking those of a leopard.
#2 - Rosettes, mimicking those of the turing patterns in many fish.
#3 - Homozygous rosettes, mimicking those of the clouded leopard with a "fill in" of a different color.
#4 - Homozygous rosettes with abstract "silly shapes", each in a different color.
Stripes (Sr)
Stripes is a dominant gene that creates many hard edged tapered lines which may point any direction. They can wrap around the legs, but on larger areas like the torso they cannot wrap around the entire body. (That's what linework is for!) Single color if heterozygous (Sr) or multicolored if homozygous (SR)
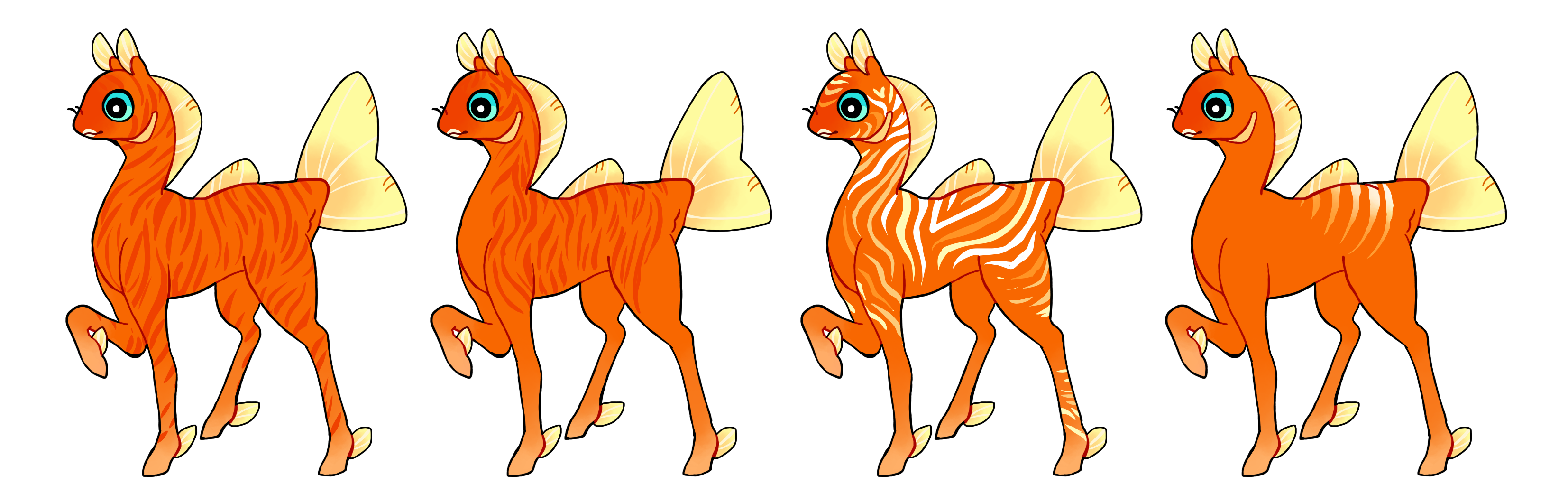

#1 - Stripes all over the body.
#2 - Stripes on only part of the body.
#3 - Homozygous stripes in different colors.
#4 - Homozygous stripes with a gradient.
Sponge (Sg)
Sponge is a dominant gene that creates hard-edged patches covered in holes, creating a weblike structure similar to a lace, sponge or an appaloosa blanket. Single color if heterozygous (Sg) or multicolored if homozygous (SG).
This gene was originally designed by trreesss for the 2024 Summer Event Gene Contest.
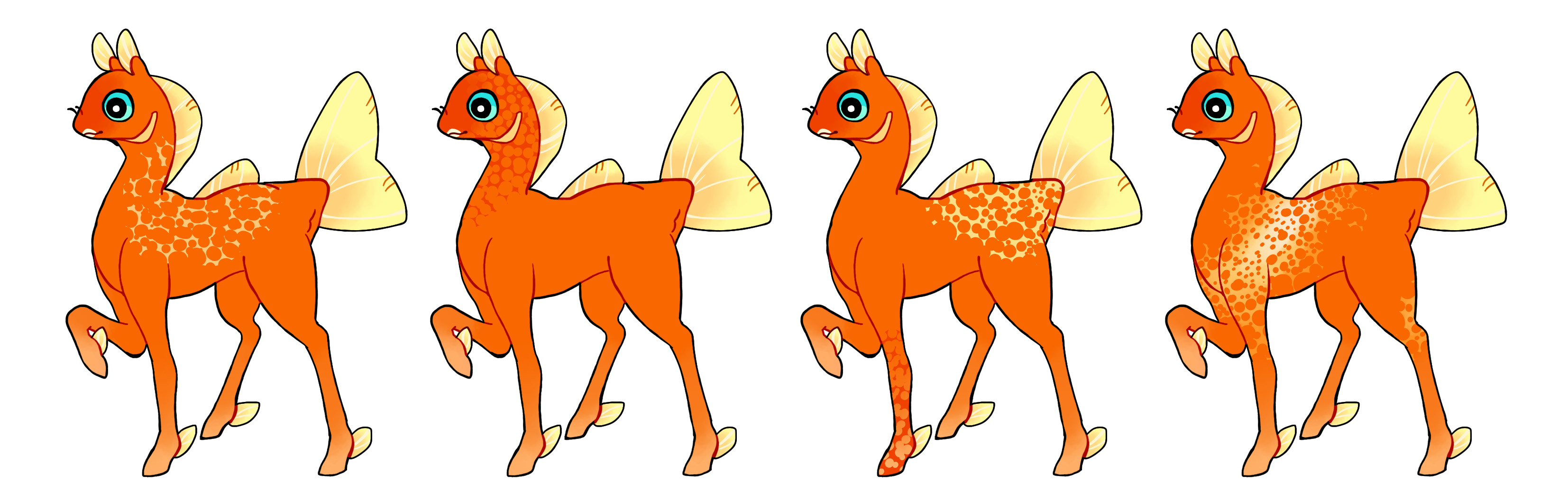

#1 - Sponge.
#2 - Sponge.
#3 - Homozygous sponge with two separate patches of different colors.
#4 - Homozygous sponge with a gradient.
Giraffe (Gr)
Giraffe is a dominant gene that creates hard-edged blocky spots similar to a giraffe's. They can be anywhere on the body. They shouldn't mimic scales or rosettes. Single-colored if heterozygous (Gr) or multicolored if homozygous (GR).
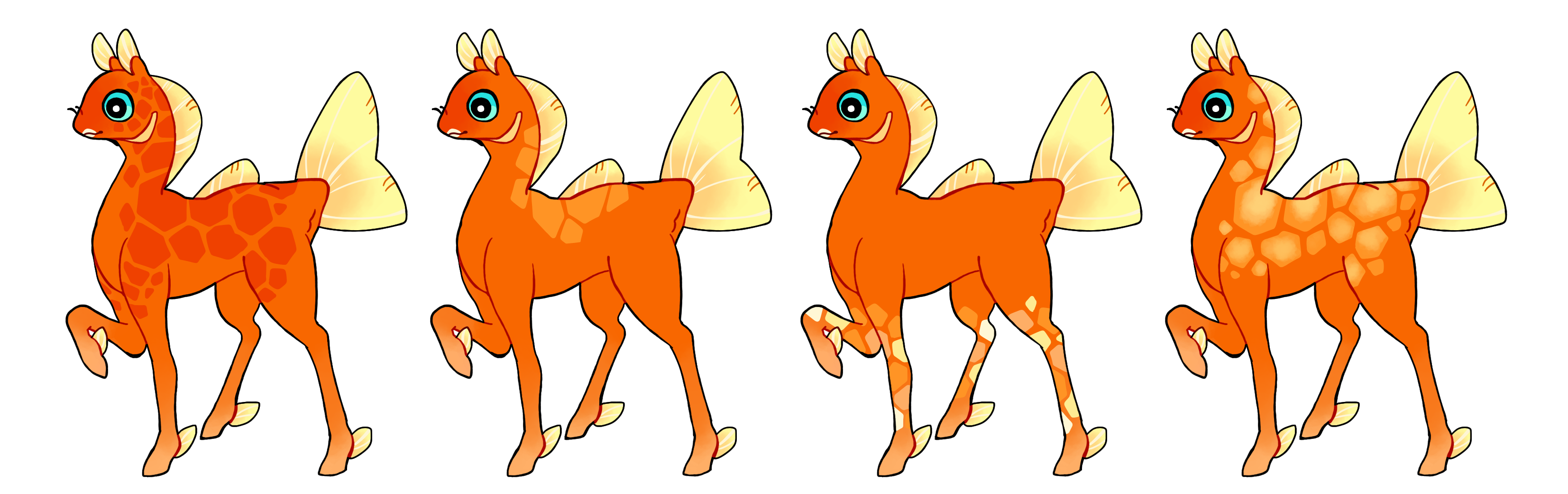

#1 - Giraffe.
#2 - Giraffe with less coverage.
#3 - Homozygous giraffe with each block being a different color.
#4 - Homozygous giraffe with a gradient.
Banded (Ba)
Banded is a dominant gene that creates large, hard edged, broad bands that wrap around a phony. The bands don't have to be present everywhere on the phony, but there must be at least one band. Bands must be thick enough to not be mistaken for Linework. Single color if heterozygous (Ba) or multicolored if homozygous (BA)
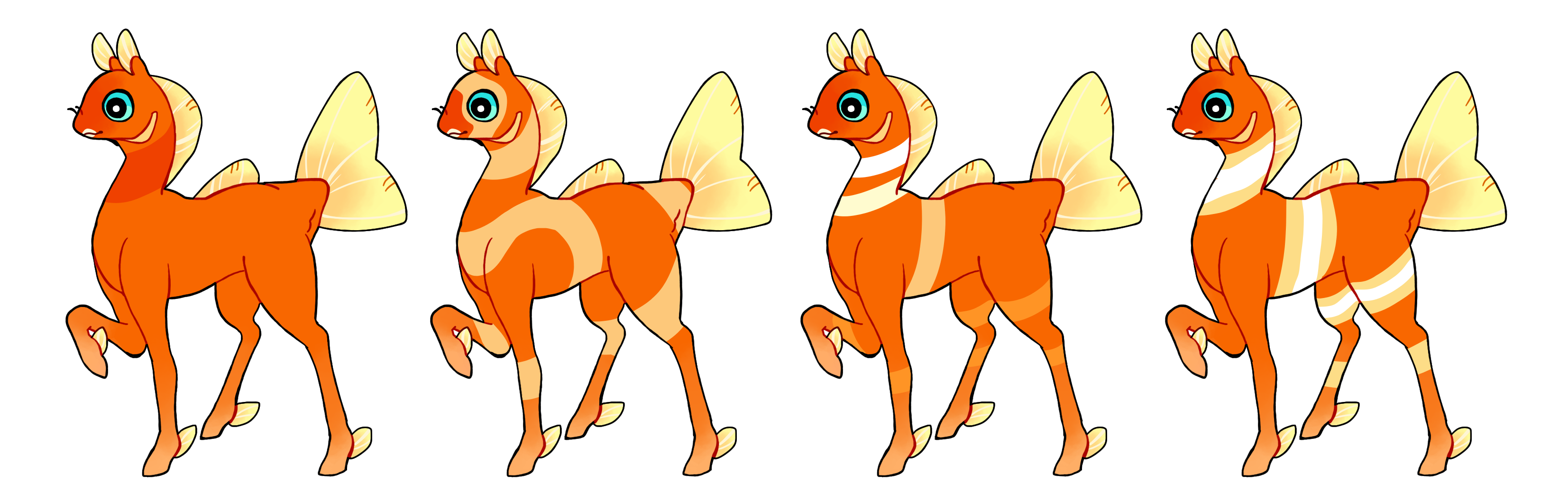

#1 - Just one band
#2 - Bands all over
#3 - Homozygous banding in different colors. Try not to have the bands much thinner than this.
#4 - Homozygous banding with multiple colors inside the band
Linework (Lw)
Linework is a dominant gene that creates numerous hard edged thin lines that wrap around a phony. These cannot stop or taper off at any point. The lines can be curved or straight, and go at any angle. The lines should not cross over or touch. The spacing of the lines and their thicknesses do not need to be identical, but the lines should not be so thick to be mistaken for Banded. Single color if heterozygous (Lw) or multicolored if homozygous (LW)
This mutation was created as a merger between Horizontal Line (Hz), Vertical Line (Ve), Free Line (Fl) and Chevron (Ch). Phonies having any of those genes will pass on Linework to offspring instead of the old line genes.
Phonies can have lines of any type at once. You could have lines going horizontally in some spots and vertically in others, provided they don't cross.
Phonies on the ML with Hz, Ve, Ch or Fl can request their genotype be updated to include Lw instead in the Import Modifications thread, and you can do the same for genotypes in the Geno Edits thread. Existing phonies can only get a visible redesign if they use an editor vial while updating the geno.
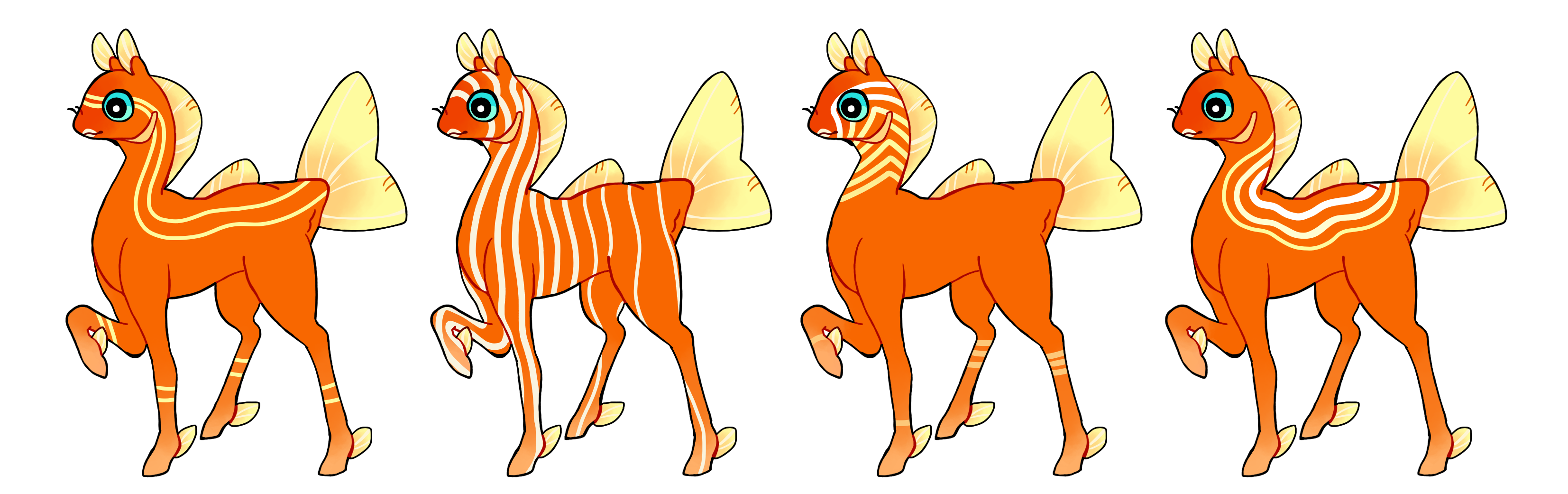

#1 - Linework going horizontally.
#2 - Linework going vertically.
#3 - Homozygous linework with a gradient and a sharp bend in it.
#4 - Homozygous linework with curves, each a different color.
Broken Trail (Bt)
Broken Trail is a dominant gene that adds hard edged lines that go in any direction (not too dissimilar from Linework) and can vary in thickness and amount. The main point with this marking is that these lines must be interrupted in some way. This can be making the line dotted, adding cuts into the line, so on and so forth. Feel free to get creative with it! Hom BT can be multitoned. Like regular linework, the lines must wrap around the phony and do not stop or taper off anywhere.
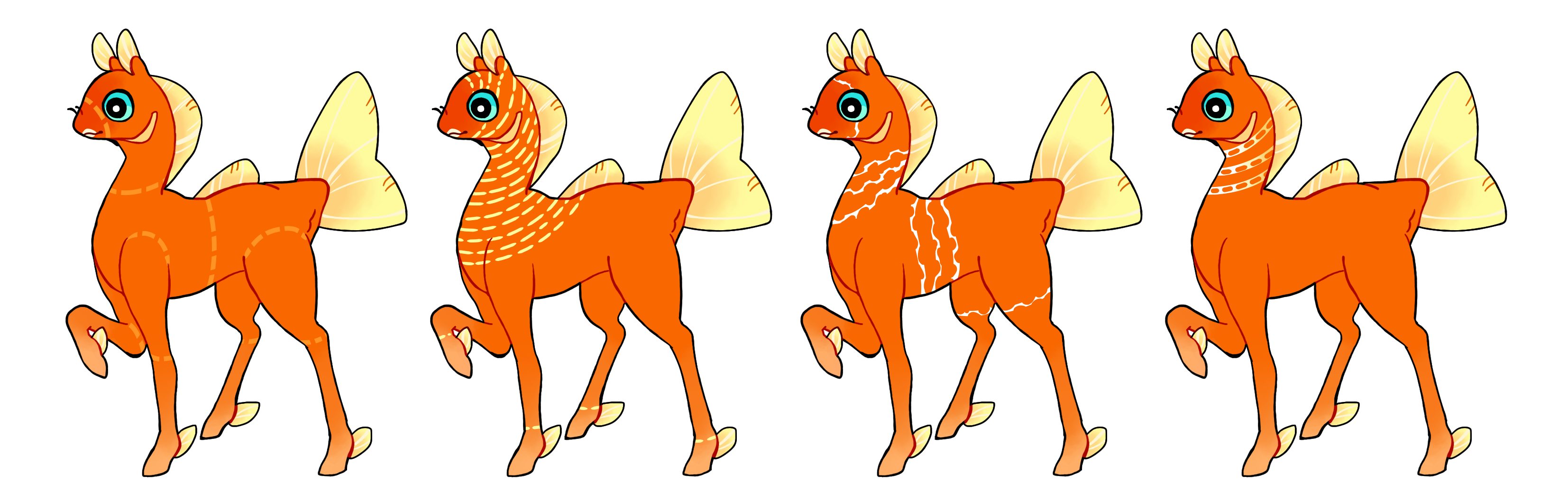

#1 - Broken trail making dashed lines.
#2 - Broken trail making a lot of dashed lines.
#3 - Broken trail making lines with "bites" taken out of them.
#4 - Homozygous broken trail making lines with holes in them, with a gradient.
Kintsugi (Kt)
Kintsugi is a dominant gene that creates hard-edged crack-like markings. These cracks cannot stop mid-body and must either connect to another crack or wrap around. Heterozygous Kintsugi (Kt) must be single-colored but Homozygous Kintsugi (KT) can be multitoned.
This gene was designed by Glitchy55 in the 2024 Summer Event's Gene Contest.
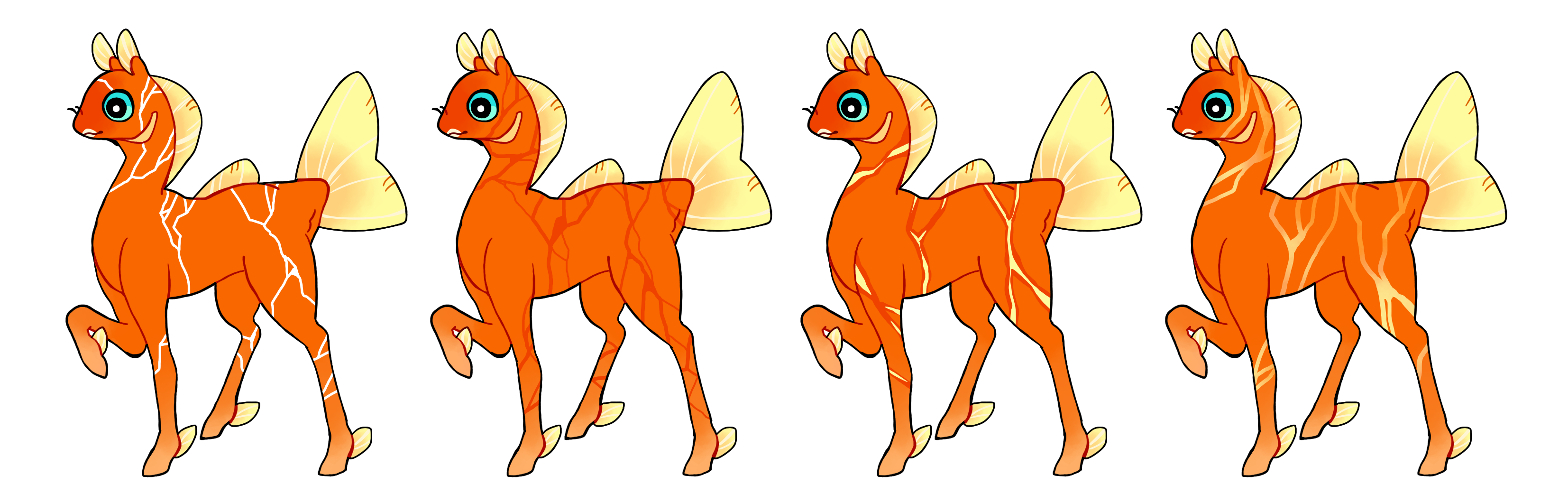

#1 - Kintsugi.
#2 - Kintsugi with cracks of different thicknesses.
#3 - Homozygous kintsugi with a different colored set of cracks inside.
#4 - Homozygous kintsugi with a gradient.
False Eye (Fe)
False eye is a dominant gene that creates a hard-edged eye-like marking. Heterozygous false eye (Fe) creates a solid color spot or ring. The spot can either be one on each side, or one on the middle of the phony. Homozygous false eye (FE) creates as many spots as desired with whatever coloring as desired.
The "Core" gene was recently merged into False Eye. Phonies with Core will pass on False Eye when breeding instead.
Phonies on the ML with Co can request their genotype be updated to include Fe instead in the Import Modifications thread, and you can do the same for genotypes in the Geno Edits thread. Existing phonies can only get a visible redesign if they use an editor vial while updating the geno.
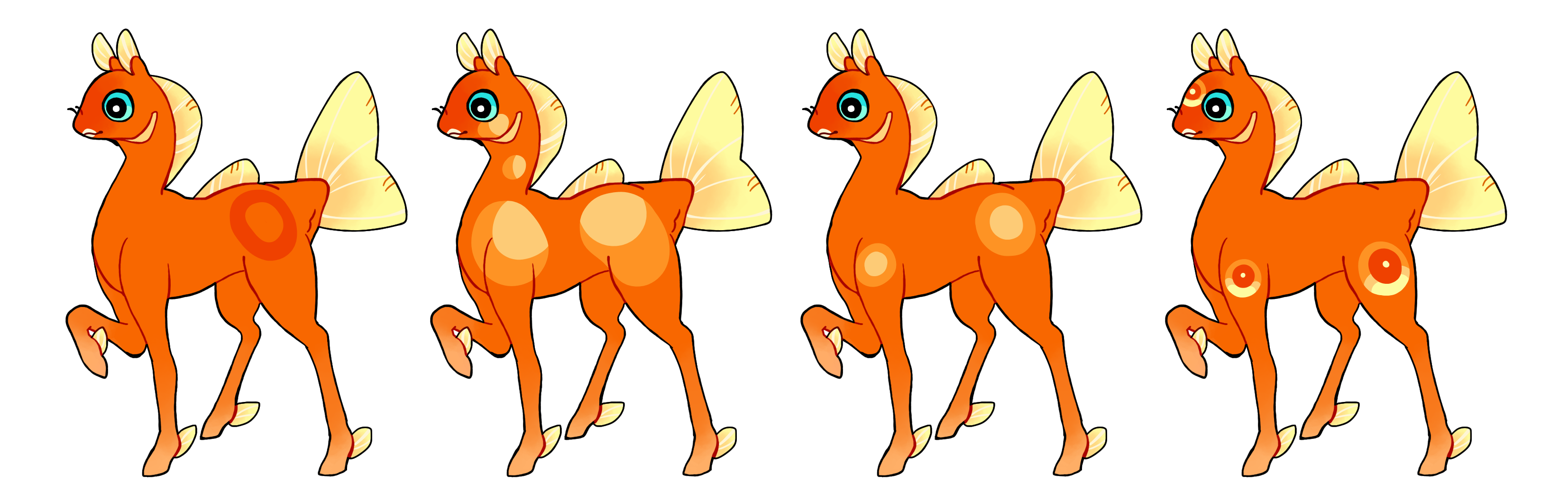

#1 - False eye.
#2 - Homozygous false eye with numerous eyes, simply duotoned.
#3 - Homozygous false eye with two eyes and a colored "fill in".
#4 - Homozygous false eye with three eyes, each colored to look like actual eyes.
Top Layer Markings
Stars (St)
Stars is a dominant marking that creates small, pinprick points on a phony which can either be circular or star shaped. They must be in random placements, and can be either lighter or darker than the base. They can be in various frequencies from occasional dots to dense freckles. Single color if heterozygous (St) or multicolored if homozygous (ST)
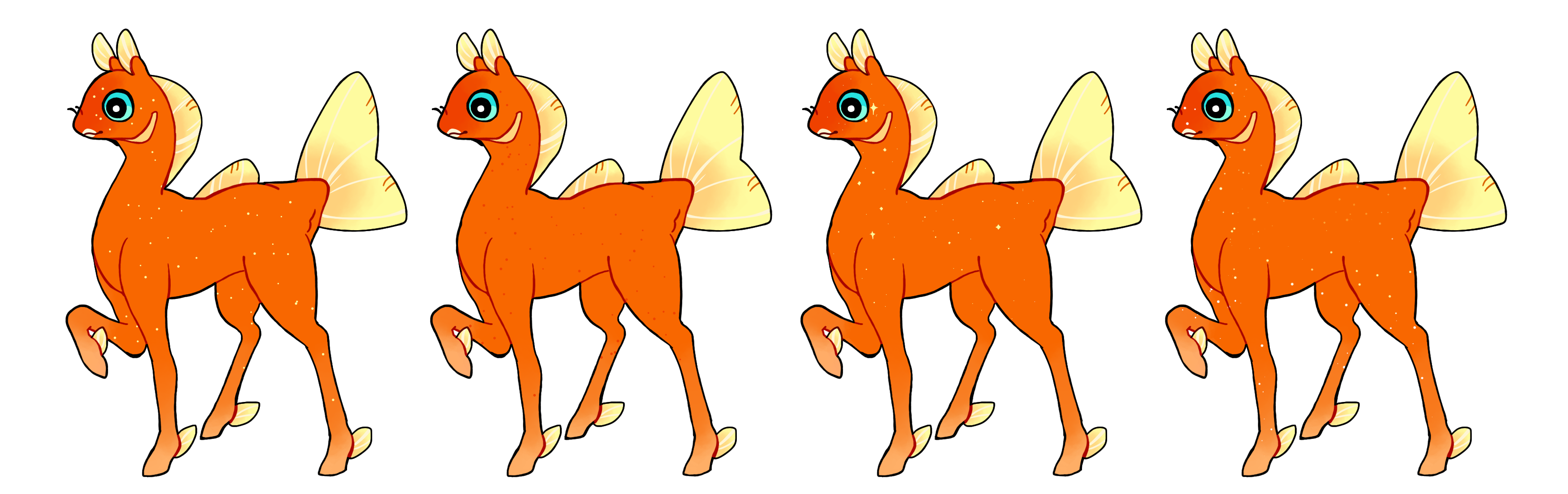

#1 - Stars.
#2 - Stars in a darker color.
#3 - Star-shaped stars.
#4 - Homozygous stars in different colors.
Trail (Tr)
Trail is a dominant marking that creates a single-file line of dot markings which travel down the phony's lateral line. Heterozygous (Tr) trail can show one trail, while homozygous (TR) can show multiple trails of dots. Dots may also connect to form dashes. Single color if heterozygous (Tr) or multicolored if homozygous (TR.)
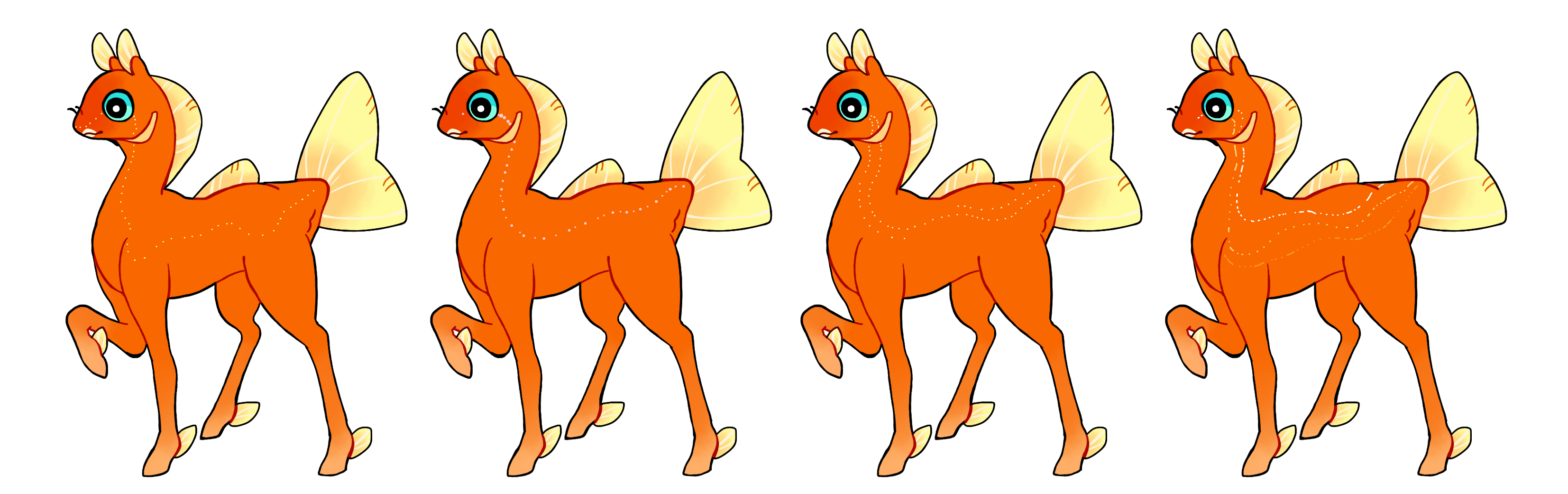

#1 - Trail.
#2 - Trail with dots of varying sizes.
#3 - Homozygous trail with multiple trails.
#4 - Homozygous trail with multiple trails and multiple colors.